Tax policy for foreign-invested enterprises
There are more and more foreign-invested enterprises in Vietnam. Similar to Vietnamese enterprises, foreign-invested enterprises must also fulfill tax obligations to the State of Vietnam. However, many foreign-invested enterprises do not yet understand what tax obligations they must fulfill. Therefore, Apolo Lawyers - Solicitors & Litigators (Hotline: (+84) 903 419 479) will provide customers with tax policy for foreign-invested enterprises when operating in Vietnam.
When doing business with a permanent establishment in Vietnam, a foreign enterprise is entitled to the following taxes:
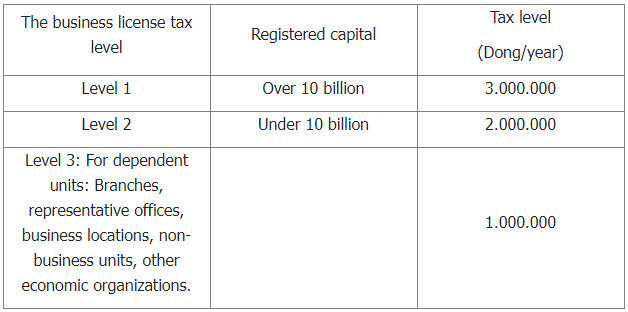
1. Business license tax
The business license tax is a direct tax imposed on entities that conduct business activities in Vietnam and are paid by the enterprises on their own on an annual basis. Business license tax helps government understand the operation situation of enterprise entities in the economy.

Depending on the amount of capital recorded on the Investment License and registered capital, each foreign-invested enterprise has a different license tax rate:
 2. Enterprises income tax
2. Enterprises income tax
According to clause 1, Article 2 of Enterprise income tax Law, foreign-invested enterprises are the enterprise income payers. Enterprise income tax is a direct tax levying on income from production and business activities and other incomes of enterprises.
Tax calculation:
Enterprise income tax payable = [Taxable income – (Tax-free income + Loss carried forward from the previous year)] × Tax rate
Taxable income = Revenue – Deductible expenses + Other income)
From January 1, 2016, the tax rate for calculating corporate income tax is 20%.
 3. Value added tax
3. Value added tax
Value-added tax is an indirect tax, levied on the added value of goods and services in the process from production, and circulation to consumption. Objects subject to value-added tax are goods and services used for production, business, and consumption in Vietnam, except for objects not subject to tax.
There are two methods of tax calculation:
Value-added tax rates have four levels: 0%, 5%, 8%, and 10%, depending on the group of goods and services.
4. Excise tax
Excise tax is an indirect tax levied on the consumption of some special goods and services that need production and consumption guidance. Excise taxpayers are organizations and individuals that produce and import goods and provide services that are subject to special consumption tax. Therefore, foreign-invested enterprises, if they trade in goods subject to excise tax, must pay tax.
Tax calculation:
Excise tax = Taxable price × Tax rate
In which, the taxable price is the selling price and service provision price exclusive of excise tax, environmental protection tax, and value-added tax. The excise tax rate ranges from 15% to 65% depending on the type of goods and services.
5. Import and Export tax
Import and export tax is an indirect tax, levied on goods imported and exported through the border gates of a country or a group of countries. If foreign-invested enterprises perform the act of exporting or importing goods, it is obliged to pay import and export tax.
There are three methods of calculating import and export tax:
Calculation method: Taxable value × Tax rate
Preferential tax rates and special preferential tax rates are specified in the tariff schedule between Vietnam and countries with preferential agreements. Normal tax rates are issued together with Decision No. 36/2016. If the goods are not on the list of normal tax rates, the tax rate of 150% applies.
Calculation method: Actual quantity of exported/imported goods × The absolute tax rate specified per unit of goods at a time
Calculation method: Total tax in percentage + Total tax calculated by the absolute method.
There are a lot of provisions in the tax policy for foreign-invested enterprises, therefore, it is not easy to fulfill tax obligations, contribute capital, and open a capital account. If you have any problems with tax and need more information, feel free to contact us to be:
For further information, please contact us: Apolo Lawyers
There are more and more foreign-invested enterprises in Vietnam. Similar to Vietnamese enterprises, foreign-invested enterprises must also fulfill tax obligations to the State of Vietnam. However, many foreign-invested enterprises do not yet understand what tax obligations they must fulfill. Therefore, Apolo Lawyers - Solicitors & Litigators (Hotline: (+84) 903 419 479) will provide customers with tax policy for foreign-invested enterprises when operating in Vietnam.
When doing business with a permanent establishment in Vietnam, a foreign enterprise is entitled to the following taxes:
1. Business license tax
The business license tax is a direct tax imposed on entities that conduct business activities in Vietnam and are paid by the enterprises on their own on an annual basis. Business license tax helps government understand the operation situation of enterprise entities in the economy.

Depending on the amount of capital recorded on the Investment License and registered capital, each foreign-invested enterprise has a different license tax rate:

According to clause 1, Article 2 of Enterprise income tax Law, foreign-invested enterprises are the enterprise income payers. Enterprise income tax is a direct tax levying on income from production and business activities and other incomes of enterprises.
Tax calculation:
Enterprise income tax payable = [Taxable income – (Tax-free income + Loss carried forward from the previous year)] × Tax rate
Taxable income = Revenue – Deductible expenses + Other income)
From January 1, 2016, the tax rate for calculating corporate income tax is 20%.
 3. Value added tax
3. Value added taxValue-added tax is an indirect tax, levied on the added value of goods and services in the process from production, and circulation to consumption. Objects subject to value-added tax are goods and services used for production, business, and consumption in Vietnam, except for objects not subject to tax.
There are two methods of tax calculation:
- Deduction method:
- Direct method:
Value-added tax rates have four levels: 0%, 5%, 8%, and 10%, depending on the group of goods and services.
4. Excise tax
Excise tax is an indirect tax levied on the consumption of some special goods and services that need production and consumption guidance. Excise taxpayers are organizations and individuals that produce and import goods and provide services that are subject to special consumption tax. Therefore, foreign-invested enterprises, if they trade in goods subject to excise tax, must pay tax.
Tax calculation:
Excise tax = Taxable price × Tax rate
In which, the taxable price is the selling price and service provision price exclusive of excise tax, environmental protection tax, and value-added tax. The excise tax rate ranges from 15% to 65% depending on the type of goods and services.
5. Import and Export tax
Import and export tax is an indirect tax, levied on goods imported and exported through the border gates of a country or a group of countries. If foreign-invested enterprises perform the act of exporting or importing goods, it is obliged to pay import and export tax.
There are three methods of calculating import and export tax:
- The percentage method:
Calculation method: Taxable value × Tax rate
Preferential tax rates and special preferential tax rates are specified in the tariff schedule between Vietnam and countries with preferential agreements. Normal tax rates are issued together with Decision No. 36/2016. If the goods are not on the list of normal tax rates, the tax rate of 150% applies.
- Absolute method:
Calculation method: Actual quantity of exported/imported goods × The absolute tax rate specified per unit of goods at a time
- Mixed method:
Calculation method: Total tax in percentage + Total tax calculated by the absolute method.
6. Tax Service at Apolo Lawyers
There are a lot of provisions in the tax policy for foreign-invested enterprises, therefore, it is not easy to fulfill tax obligations, contribute capital, and open a capital account. If you have any problems with tax and need more information, feel free to contact us to be:
- Guiding and making tax declarations for newly established foreign-invested enterprises;
- Working on behalf of the client with the tax authority regarding the initial tax declaration, the procedure for printing and ordering the first printing of invoices;
- Consulting on tax accounting for foreign-invested companies on a quarterly, monthly, and yearly basis;
- Declare and pay all kinds of reports, taxes by month, quarter, year, finalization of taxes for foreign-invested companies;
- Prepare and complete the accounting system for foreign-invested companies in accordance with current laws;
- General advice on issues related to value-added tax, corporate income tax, personal income tax,...;
- Advising on the adjustment of errors in accounting and tax activities of enterprises;
- Representing clients to work and explain tax declaration and reporting issues to state agencies;
For further information, please contact us: Apolo Lawyers